BlogGuide
The Guide to Generative AI Agents
August 7, 2024


Written by Jesse Zhang
This post is a broad overview of the answers to these questions and why so many companies are choosing to partner with new AI agent solutions rather than older incumbents.
Decagon enables large companies (like Rippling, Eventbrite, Bilt, etc) to deploy AI agents to handle customer support and experience. You can learn more about us here.
What are AI Agents?
Traditional software applications were designed to make your work easier—to help you look up information, analyze data, or draft a report. But in each case, the work itself still depended on you.
AI agents change that. These are autonomous systems capable of reasoning, making decisions, and achieving goals with creativity and flexibility, all while adhering to the boundaries set for them. While traditional applications assist you in doing the work, AI agents do the work for you.
A Brief History
On the backend, tools were available to assist human agents by making their work more efficient—offering templates, categorizing tickets, or retrieving information from knowledge bases. But ultimately, the human agent was always in control.
Generative AI agents take this a step further. They can autonomously handle entire processes: crafting personalized responses, retrieving data, executing actions, and even analyzing conversations post-interaction. They don’t just assist—they manage the entire workflow from start to finish.
This capability is the real breakthrough of this new generation of AI agents. By relying on software to complete entire jobs, we fundamentally transform how work gets done.
How Does Generative AI Fit In?
You’ve likely seen these models in action—solving difficult questions, creating detailed responses, or even generating creative content. When used effectively, these LLMs enable generative AI agents to do more than just chat; they allow the agents to get the job done.
The Anatomy of an AI Agent
- Orchestration: This layer acts as the agent’s nervous system, guiding its actions and ensuring it follows the business logic specific to each customer. Orchestration integrates the AI models with the company’s goals, making sure the agent’s actions are not just correct, but also aligned with what the business needs.
- Data Sources and Tools: Think of these as the agent’s muscles. They provide the strength necessary to perform tasks—whether that’s retrieving data from a CRM, processing a transaction, or interacting with specialized tools. This layer allows the agent to be customized and effective in performing the specific tasks required by each business.
- Hallucination Protection: This acts as the agent’s immune system, safeguarding against errors that could arise from the non-deterministic nature of AI models. Enterprises require robust guardrails to maintain the trustworthiness and reliability of their generative AI agents.
- Continuous Learning: This is the agent’s sensory system, constantly taking in feedback and adapting to improve its performance over time. A well-designed continuous learning loop enables the agent to refine its responses, update its knowledge base, and continually evolve to meet new challenges.
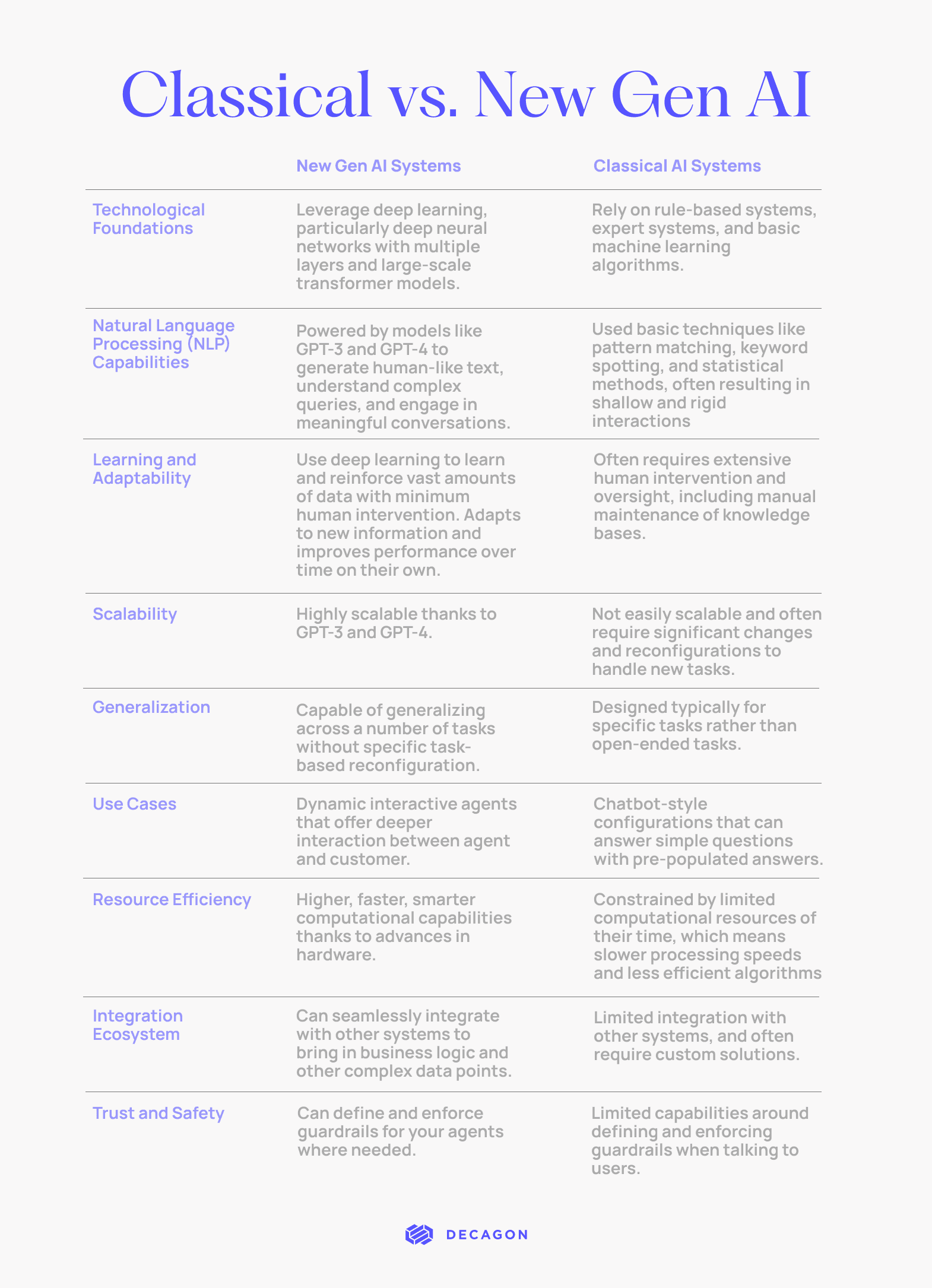
Classical AI vs. Generative AI: What’s the Difference?
To help navigate this shift, we’ve put together a simple guide comparing the differences between classical AI and Generative AI. By understanding these differences, companies can make better decisions about how to leverage AI to drive innovation and improve customer experiences.
In 10 Years, Every Company Will Run on Generative AI Agents
Book a demo
The future of customer experience
starts here.
starts here.
